Neuromuscular connection – what is it?
Neuromuscular connection is the conscious ability to feel your muscles and increase their level of involvement during exercise. It is the developed neuromuscular connection that distinguishes a beginner who lifts a weight due to the force of inertia from a professional athlete who uses the body’s capabilities 100%. Ultimately, the muscle-to-brain connection helps you train effectively.
To improve neuromuscular communication, it is necessary to take into account the fact that there are different types of muscle fibers . Slow (red) fibers develop when doing static exercises, while fast (white) fibers develop their strength when properly performed dynamic exercises. When training, it is necessary to combine different types of loads.
Professional bodybuilding also pays attention to the development of neuromuscular connection – it is this connection that allows you to pose in competitions and consciously strain certain muscle groups. In particular, this is especially important for the volume of the arms and chest. The role is also played by the fact that in the absence of communication between muscles and the brain, the symmetry of the body is disrupted – which is undesirable for bodybuilders.
// What the neuromuscular connection gives:
- Ability to deliberately tense muscles
- More correct exercise
- Improving muscle symmetry
Functional training
Since the development of the dough’s neuromuscular connection is associated with conscious exercise, functional training is better suited for this than strength machines. For example, when doing pull-ups on the bar, the athlete learns to engage the latissimus dorsi, while when performing the pull-up of the upper block in the simulator, many beginners pull the weight solely with the strength of the arms.
In fact, strength training with excessively large working weights only impairs neuromuscular communication, rather than developing it at all. Trying to train “to failure” (when there is no energy left for the last repetition) significantly increases the risk of injury – although, in theory, this should create stress, provoking hypertrophy processes and causing muscle growth.
How to learn to feel the biceps?
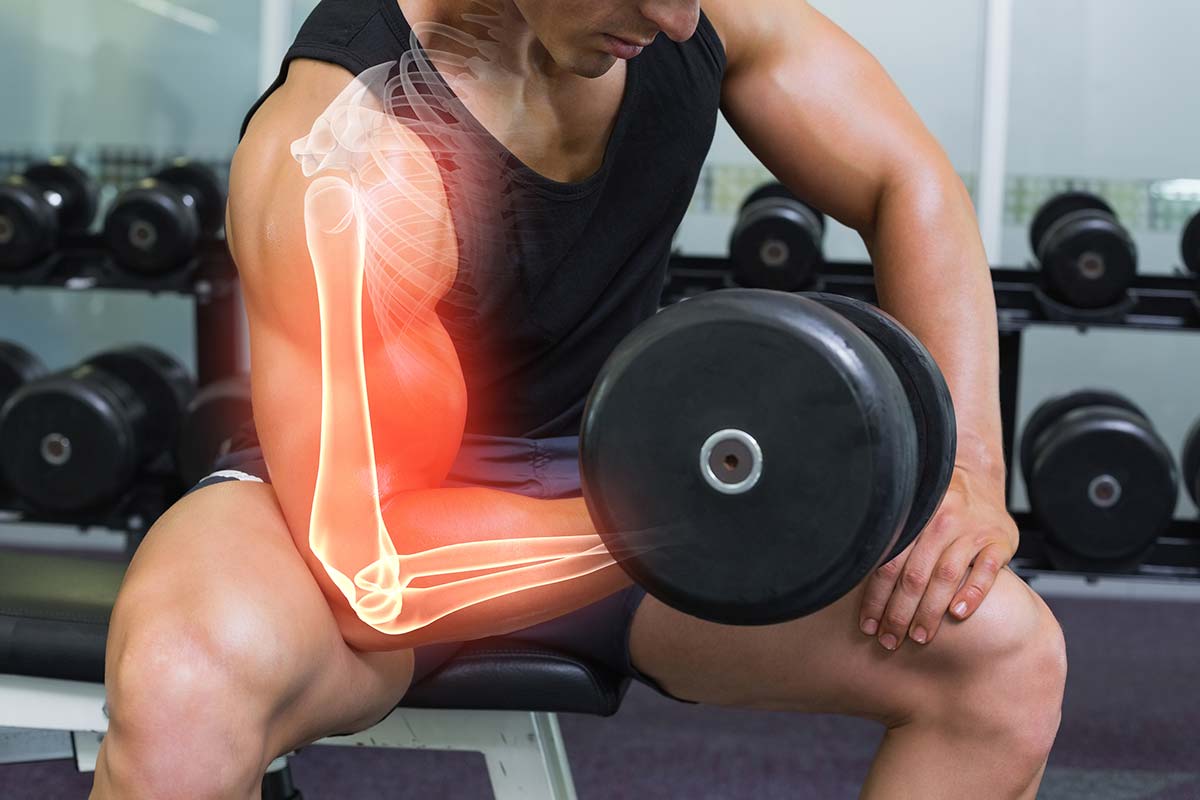
The reason why many beginners do not feel the work of the biceps in exercises and cannot pump it up is banal – excessive working weight. The use of overly heavy dumbbells does not allow the exercises to be performed correctly and leads to various postural disorders, and not at all to the desired muscle gain. In order to build biceps, you first need to develop a neuromuscular connection.
Effective biceps training begins with concentration on exercise technique and moderate working weight. The first approaches of each exercise are recommended to be performed with empty hands, without weight, while trying to imagine that you are lifting a lot of weight. However, this approach to training seems too easy for beginners, and they tend to quickly move to heavy exercises.
How to properly strain your muscles?
Before performing basic exercises, beginners are advised to perform several approaches with minimal weight. For example, before barbell squats, you need to do 2 sets of squats with arms extended forward – 10-15 slow reps each. During such squats, it is necessary to strain the abs, the muscles of the buttocks and hips – this will strengthen the connection of the muscles with the brain.
Before doing the bench press (or any other strength exercises on the chest), a warm-up in the form of light push-ups or dumbbell dilutions is also necessary. Try to “catch” exactly the movement in which you feel the maximum muscle tension and their involvement in work – in the future, when working with weight, try to recreate this feeling of neuromuscular connection.
Methods for the development of neuromuscular communication

Concentration and visualization are key techniques for developing neuromuscular communication. When doing exercises and lifting weights, you should imagine how the muscle tenses and relaxes, how blood circulates during contractions. If you find it difficult to visualize these processes, place your hand on a working muscle and feel its work.
Concentration, in turn, implies full mental commitment to training. If the thought is spinning in your head about how to finish the repetition faster and respond to the next message in the messenger, it is difficult to talk about the development of the connection between the brain and muscles. During your workout, you should focus solely on one thing – how to do it as efficiently as possible.
The positive effect of pumping
Another method of strengthening the connection between muscles and the brain is pumping – that is, pumping and increasing the volume of the working muscle by increasing blood flow. The greater the physical volume of a muscle, the easier it is to feel its work and control this work mentally.
Both special sports nutrition – pre – workout complexes and exercises with low weight and high repetitions (for example, a combination of a bench press with a barbell and push-ups from the floor) can increase blood flow in the muscles .
Muscle memory development
The good news is that the development of neuromuscular connections correlates with the development of muscle memory – once you learn to feel your muscles and strain it with willpower, you cannot lose these skills even after years of lack of strength training.
It is because of the presence of muscle memory and good neuromuscular connections that athletes are able to regain muscle volume in the shortest possible time. Let us also recall that muscle growth is largely associated with the ability to engage muscle fibers in the work, and not with an increase in their number.



